The prevalence of mycoid diseases has made them recognizable and easily treatable ailments in their early stages. But the signs of foot fungus themselves, indicating the onset of infection, are not familiar to every person. After all, there are about fifty varieties of fungus alone. But there is also a broad category of skin diseases - epidermycosis. Therefore, in order to prevent the disease from developing to a state dangerous to the health of the body, it is necessary to study its features.
General signs
Fungal skin infections rank first among ailments affecting the epidermis. Its signs are quite recognizable. The main difficulty in the diagnostic process is establishing the exact type of fungal infection. This is required since each of them is resistant to a certain group of antifungal drugs. Therefore, in order to carry out treatment, a mandatory visit to the doctor is necessary. Accurate identification of the mycoid group is impossible without special biological research.
The following signs may be a reason to contact a specialist:
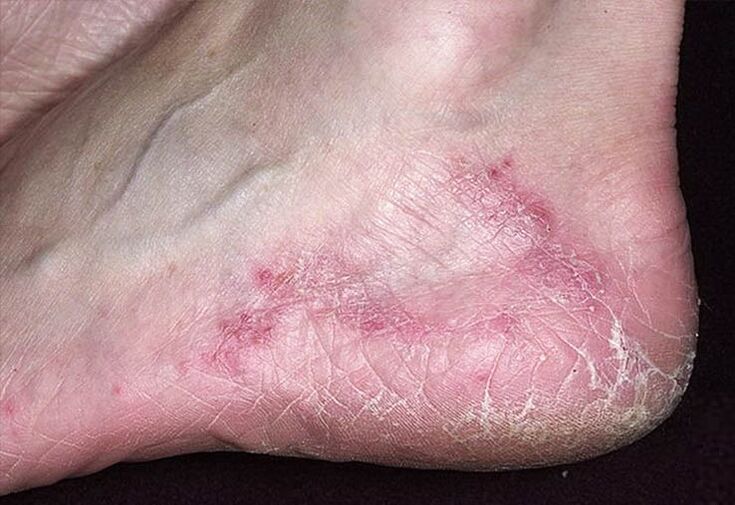
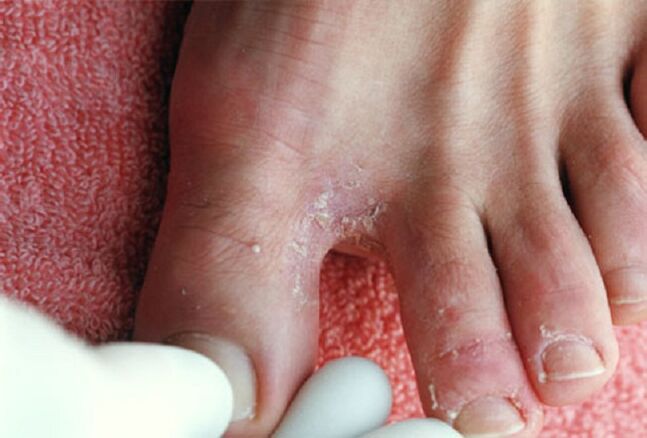
- Cracks in the epidermis between the toes. It is this area that is considered most at risk of fungal infection. Additional evidence of infection may include excessive dry skin, flaking of the feet and pain.
- Noticeable thickening and roughening of the skin layer. Similar symptoms are observed when a corn or dry callus forms. But in some cases, the cause of this change is a fungus.
- Destruction of the skin, blisters. Such injuries are often first diagnosed on one leg and subsequently appear on the other.
- Redness of the epidermis, itching or burning sensation. This set of symptoms is considered one of the main signals confirming a fungal infection. The difficulty of diagnosis in this case lies in the fact that each type of mycoid causes such a set of symptoms.
- Change in color of the nail plate.
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor in the infected area.
It is important to detect the first signs of fungus in time, since the disease is very difficult to treat, and it is easy to become infected.
Mycoid infection quite easily penetrates the body, infecting internal organs and systems. This explains the frequent relapses of the disease in the complete absence of external provoking factors.
Medical classification
Mycosis fungoides is classified according to its characteristic features into four main forms.
For each form of foot fungus, the symptoms vary depending on what it is:
- Squamous.
- Dyshidrotic.
- Intertriginous.
- "Classic" onychomycosis.
The squamous or scaly form of fungal infection is considered one of the initial stages of infection. Skin lesions in this case are first observed on one foot. Over time, a second infection occurs. The main symptom of the scaly form is redness of the skin, which subsequently develops into keratinization of inflamed tissue areas. Without treatment, the squamous form develops into a dyshidrotic form.
The dyshidrotic form of mycoid infection has a pronounced characteristic feature - the appearance of small bubbles in the affected area. After opening, the blisters become inflamed, forming a stable focus of erosion of the upper layers of the skin. The patient usually experiences severe itching; in fairly advanced cases, it gives way to pain. The skin begins to peel off and erosions form regularly. This form of the disease can develop into the first squamous form without any system. Because of this, some experts believe that the forms of mycosis fungoides mentioned are two forms of the same type of infection.
The intertriginous form of infectious fungal infection is the most common. Manifestations of the disease include the appearance of cracks in the skin of the feet, visible to the naked eye, and the formation of exfoliated areas of white skin on their edges. For the interdigital area, a characteristic sign of the intertriginous form is the formation of weeping spots and erosion of the epidermis. The patient constantly experiences itching in the infected area. Treatment of this form of infection is complex and lengthy, since the disease most often takes on a chronic form.
Onychomycosis is an infectious infection, the symptoms of which are given special attention. Depending on the characteristics of the pathology, the type of damage to the nail plate and the type of disease change. There are three main types of onychomycosis:
- Hypertrophic - the nail plate gradually collapses, its color changes to yellowish, and characteristic spots appear. Pain in the affected area appears after deformation of the nail.
- Normotrophic - destruction or change in the shape of the nail plate does not occur, spots or lines of yellowish and white color appear on it.
- Atrophic is the most dangerous form for the nail plate, in which it is severely destroyed, deformed and often peels off from the nail bed.
Each form of onychomycosis has its own general treatment regimen. But in order to completely get rid of the infection without consequences for the body and to exclude a relapse, it is recommended to carry out treatment on the recommendation and under the supervision of a doctor.
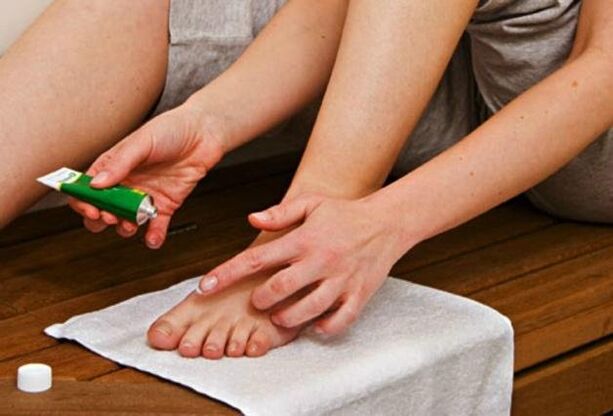
Treatment methods
In most cases, it is possible to completely get rid of a disease detected in time in a maximum of a month. This is a very important point in treatment, since itching, tissue damage and other manifestations disappear, the patient sometimes stops treatment, believing that the disease has been defeated. But remnants of the infection can easily trigger a relapse.
Treatment procedures should be stopped only after the doctor’s permission and after passing the necessary tests. This is especially true for advanced forms of the disease. The fungus is firmly "fixed" in the body and sometimes it can take at least six months to get rid of it. But the external manifestation of fungus on the feet in the form of various damage to the skin or nail disappears much earlier, creating the illusion of health. By stopping therapy in this case, the patient is almost guaranteed to provoke a relapse.
Treatment of feet for mycoid infection is carried out comprehensively. To get rid of the disease, local antifungal drugs and tablets are used to eliminate the infectious agent that has penetrated inside the body. To get rid of itching, pain, brittle nails and accelerate tissue regeneration, certain medications may be prescribed. It is not recommended to combine them independently with the main therapeutic group, so as not to provoke an allergic reaction or poisoning of the body due to the simultaneous use of incompatible drugs.
Cure foot fungus at an early stage is quite simple. Usually, two weeks of therapy is sufficient to eliminate the symptoms of mycoid infection.

Duration of treatment
Combined infection of the skin and nail plate requires rehabilitation therapy for one to three months. These terms are considered standard for the most effective pharmaceutical products from a medical point of view.
Pregnancy requires a mandatory visit to the doctor to choose a method of getting rid of mycoid infection. Potent medications and therapies that require the use of similar medications are prescribed only under the supervision of a physician in compliance with strict dosages. Many antibacterial tablets that effectively destroy fungus can cause noticeable harm to the fetus. Therefore, whenever possible, during pregnancy, patients are recommended to be treated using traditional medicine recipes. Many of them allow you to cope with the disease, but provided that the disease has not reached a complex stage. Only classical medicine can help cope with the advanced form.
Modern medications allow you to completely restore your legs to health within two weeks, provided that signs of infection were detected in time.

Preventive measures
Preventing a disease is always easier and safer for health than treating it, even using the most gentle method. In the case of a fungal infection, prevention is one of the mandatory norms of life, since it is very easy to become infected. Therefore, to reduce the risk of contracting the disease, it is recommended to follow a few simple rules:
- try to eat right, eating healthy foods whenever possible;
- do not use other people’s things and personal hygiene products;
- use basic protective equipment in public places, such as replacement shoes and hygienic antibacterial agents;
- wash your feet and change your socks regularly;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Take regular baths to improve foot health;
- periodically disinfect shoes.
Prevention of fungal infection is important not only to prevent it, but also if the disease does occur. In this situation, compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards helps speed up healing and prevent infection of others with the fungus.